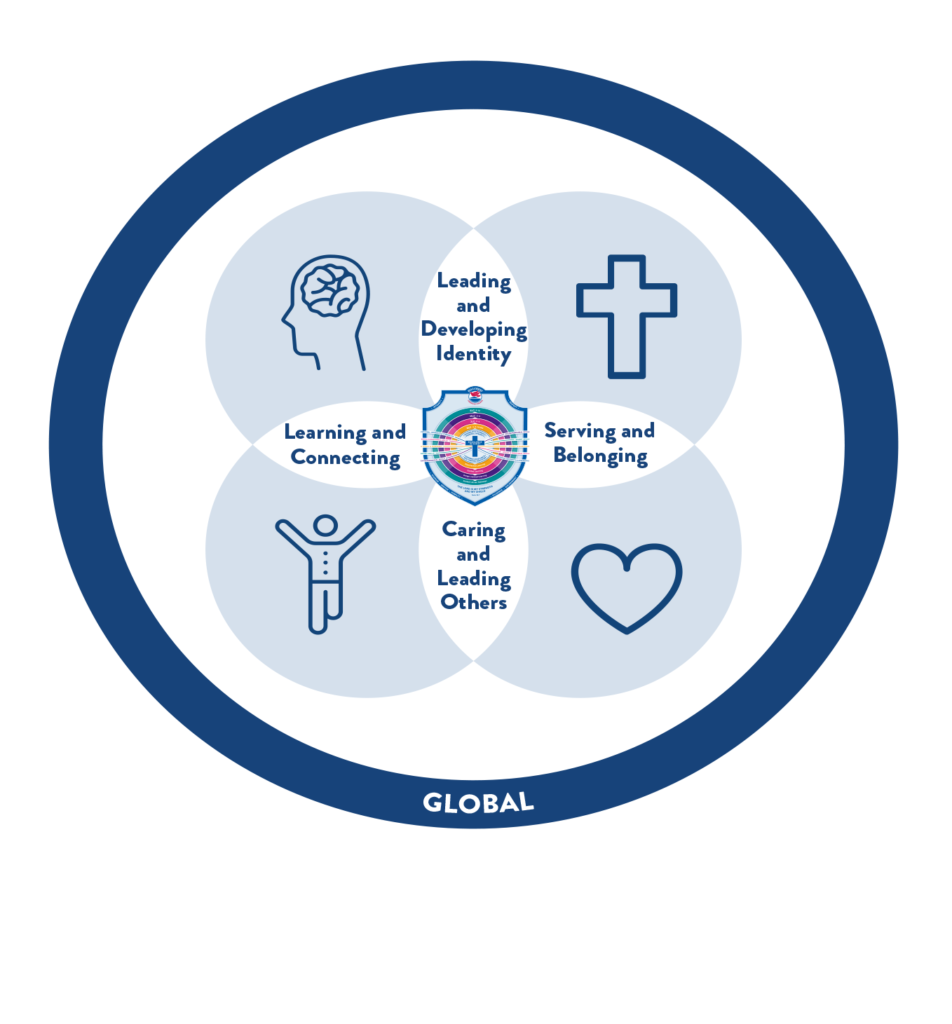
Connecting Communities Through Innovative Education
Jeff Davis - Future Focused (SESSION ONE)
Each phase of learning is underpinned by a combination of the following elements of learning with a view to help foster meaningful experiences for students:
‘FUTURE FOCUSED’ SYNOPSIS
Education has always played a crucial role in shaping the society we live in today. Throughout history, the way education was approached and delivered has changed drastically, reflecting the values and beliefs of the time. As we look to the future, we need to be cognisant of the next wave of technological changes that will be reflected in the education processes of the future.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly becoming an integral part of our daily lives, and the education sector is no exception. Schools need to adapt to this shift in technology to prepare students for the future. There are a few key changes educators can make to best adapt:
- Introducing AI Education as part of the curriculum to ensure that students are prepared for the future. The curriculum should include topics such as machine learning, data analysis, and programming languages that support AI technology.
- Upgrading infrastructure to effectively teach AI. Schools could benefit from upgrading to the necessary hardware and software infrastructure. Investments into high-speed internet connections, AI-powered devices such as robots, and other necessary tools would be an asset.
- Redefining teaching and learning methods to respond to the advances AI is making. Teachers will likely need to adapt to new teaching strategies that involve technology. Schools could integrate AI into the curriculum to offer personalized learning experiences to students.
- Developing critical thinking skills could be easier and more efficient with the help of AI. However, it is essential to teach students to think critically about the use of AI. Students should understand how AI works, its potential benefits and limitations, and its ethical implications.
- Preparing students for the job market is evolving as a result of how AI is transforming workplaces. Students should have the necessary skills to adapt to the changing job market and the ability to work with AI technology. The changes mentioned above will allow students to better prepare for the future, utilising AI technology to their advantage.
In addition to intellectual skills, social and emotional skills are equally essential for students’ success in school and beyond.

Jeff Davis
Principal

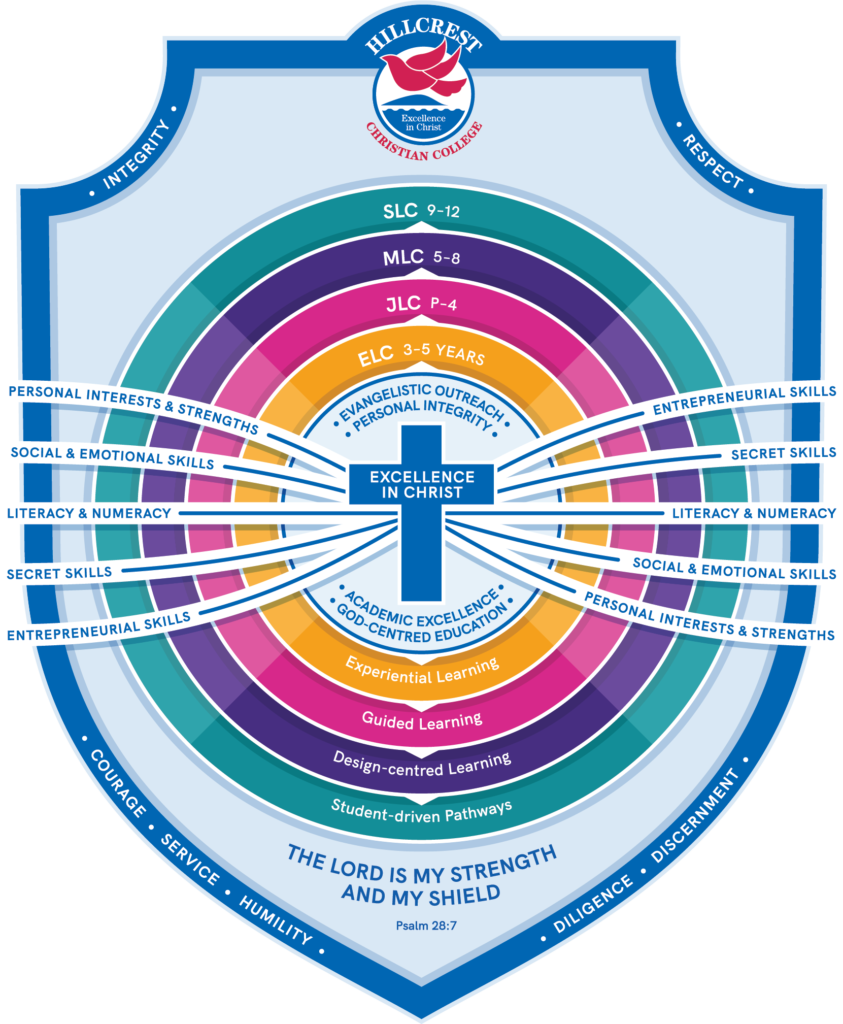
Educational Structure
EARLY LEARNING COMMUNITY – EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING AGES 3 – 5
This community endeavours to create a positive disposition towards learning where children can grow and develop into competent and confident learners in a dynamic, experiential learning environment; responsive to their strengths, needs, abilities, and interests.
JUNIOR LEARNING COMMUNITY – GUIDED LEARNING PREP – YEAR 4
Guided learning blends a model of explicit instruction and active ‘hands-on’ learning to engage children as they develop knowledge and explore key foundational skills. Guided learning leads children to increasing independence and autonomy as confident learners who have knowledge and skills to embrace an ever-changing world.
MIDDLE LEARNING COMMUNITY – DESIGN-CENTRED LEARNING YEARS 5 – 8
This community is founded in a middle schooling philosophy based on building relationships and student engagement while focusing on preparing future-focused learners. At a stage where students are undergoing many physical, social, and emotional changes, students require a focused approach to meet their specific needs.
SENIOR LEARNING COMMUNITY – STUDENT-DRIVEN PATHWAYS YEARS 9 – 12
This is the final phase of education at Hillcrest. Students are guided through the art of goal-setting, and meeting the higher expectations of independence, responsibility, self-motivation, and self-discipline. The College provides students options to follow their desired pathway. This flexibility fosters personal interests and strengths, and combined with staff support, provides the necessary road map to drive students towards their future goals.




Foundational
Values
INTEGRITY – I do what is right even when no one is looking.
RESPECT – I treat others the way I wish to be treated.
COURAGE – I stand up for others and what is right.
SERVICE – I look to serve others in the community.
HUMILITY – I admit my mistakes and learn.
DILIGENCE – I am prepared for and work productively in class.
DISCERNMENT – I ask myself “Is this a wise decision?”


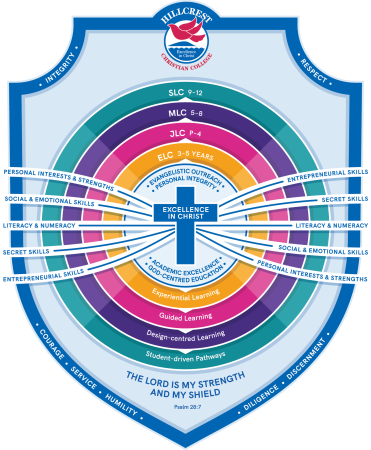
Elements of Learning
Each phase of learning is underpinned by a combination of the following elements of learning with a view to help foster meaningful experiences for students:
PERSONAL INTERESTS AND STRENGTHS
Hillcrest connects with personal strengths to drive engagement for students to achieve academic and personal growth. By leveraging personal interests in the classroom, students fuse existing knowledge with new information to form authentic and lasting connections.
SOCIAL AND EMOTIONAL SKILLS
Hillcrest believes that social and emotional skills are critical to the development of a child’s academic outcomes, skills for success, and mental health and wellbeing. Social and emotional skills, including resilience, self-efficacy, critical thinking, and self-regulation, have been shown to be malleable and highly predictive of success in a wide range of important life outcomes.
LITERACY AND NUMERACY SKILLS
Hillcrest understands the teaching of literacy and numeracy skills are the responsibility of all as they form the basis of our learning in everyday life, and underpin the acquisition of more complex skills such as critical and creative thinking.
SECRET SKILLS
The SECRET Skills framework comprises 24 essential skills that have been identified through research as critical to driving personal growth. Comprised of six skill domains: Self-Manager, Effective Participator, Creative Thinker, Reflective Learner, Enquirer, and Team Worker. This framework is self and peer-assessed; while teachers facilitate and encourage students to achieve their goals.
ENTREPRENEURIAL SKILLS
Entrepreneurial skills responds to the growing need to enhance student capabilities to adapt and apply knowledge to solve problems in unique ways. The skills that are developed through this style of problem solving allow students to meet everyday challenges, and experience growth as they apply their knowledge in new ways.

Joy Geyer
Head of Culture & Wellbeing

Joy Geyer - Wellbeing (SESSION TWO)
BIOGRAPHY
Joy is passionate about education and its capacity to help individuals flourish through finding their gifts and talents, and learning to lead themselves, and others to high levels of wellbeing. She has a broad number of experiences in leading staff, students, and families through strategic initiatives having been the Head of Primary (Kindy – Year 6) for many years before moving into her current role across the College. Joy has recently completed a Master of Educational Leadership, majoring in Wellbeing, and is committed to developing ways to build sustainable systemic change across cultures.
SYNOPSIS
Social and emotional skills are equally essential for students’ success in school and beyond. Social and emotional skills refer to the ability to manage emotions, build relationships, and make responsible decisions. These skills are also crucial in the workplace, where individuals need to work collaboratively, communicate effectively, and adapt to changing situations. Therefore, integrating social and emotional skills into the curriculum is crucial to ensuring students’ academic and personal success.
Educational Model
At the centre is our Educational Model, a vision which from the last 35 years has come together to outwork our programs and education ethos in conjunction with our executive team.
WELLBEING
Where individuals realise their potential, cope with normal stresses of life, work productively and contribute to community.
![]()
‘Social Emotional Learning’ skills such as self-management, self-awareness, decision-making, relationship skills, social awareness.
![]()
The moral compass and the values-driven nature of a person (Service Mindset, Biblical Worldview and Biblical Literacy).
![]()
Ability to reason, solve problems and demonstrate knowledge in known and unknown situations.
![]()
Contexualising one’s skills needed to be effective in their current environment and into the future (Innovation, SECRET Skills, Real World Learning).